With the introduction of the Modbus Scanner in E-Series Utilities 8.12.4, the SCADAPack E is able to be a Modbus Master for Modbus RTU or Modbus/TCP Client protocols.
In cases where there might be a challenge communicating to a slave device, the Command line Interface and MODBUSDIAG may be used to troubleshoot the Modbus communication protocol. The Diagnostic Command Line Interface can only be accessed via Telnet or a serial port configured as “CMD Line”. The example below will use “CMD Line” port mode.
Use the MODBUSDIAG command to filter Modbus protocol diagnostics when you are in a diagnostic display session and the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master or a Modbus/TCP Client.
A Modbus RTU Master communicates with a Modbus RTU Slave using the Modbus RTU protocol over a serial port.
A Modbus/TCP Client communicates with a Modbus/TCP Server using the Modbus/TCP protocol over an Ethernet port, or using PPP/TCPIP over a serial port.
Hexadecimal format is used to display protocol data bytes.
To enter or return to a diagnostic display session, type DIAG at the command prompt.
MODBUSDIAG mode filter [filter ....]
Where: mode = ENABLE DISABLE
Where: filter = * TX RX ERROR TCP_CLIENT SERIAL_MASTER
Using diagnostics can impact system performance. As a result, you may want to disable diagnostics when not in use. The following system diagnostic filters can be individually enabled or disabled, and are retained in non-volatile memory.
The system design will be as follows:
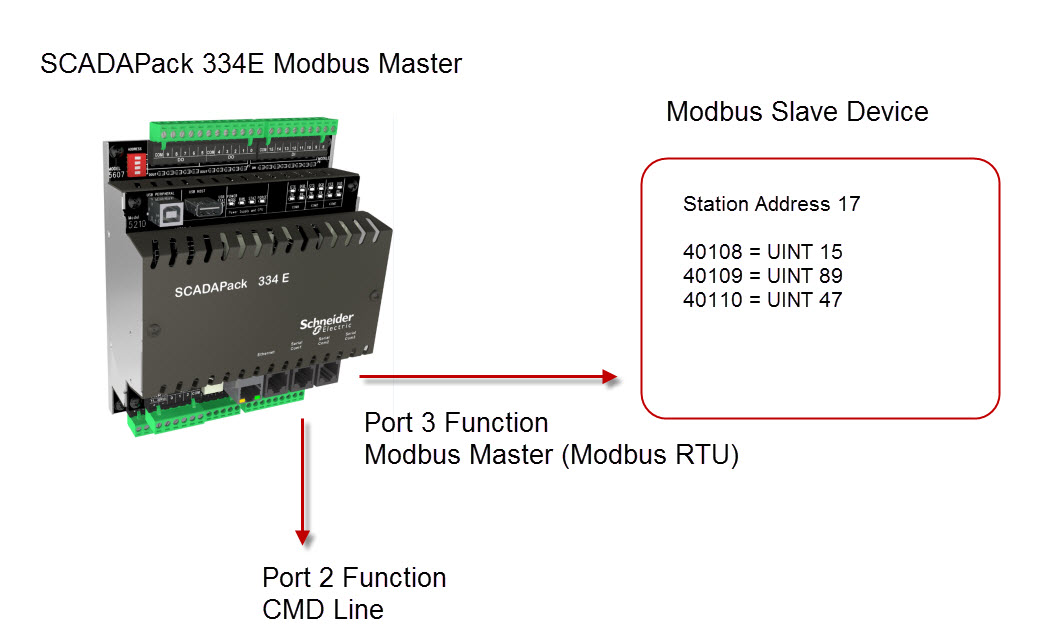
By connecting to the Command Line Interface port with a terminal program you can use the MODBUSDIAG command to see the Modbus messages to the slave device.
MODBUSDIAGS Enabled: TX RX ERROR SERIAL_MASTER
2. Start streaming diagnostics on the serial port (diag).
C:\>diag
Connecting to diagnostic display. Use <ESC> to disconnect
16:25:11.286 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:11.353 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:12.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:12.348 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:13.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:13.365 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
The actual windows in the terminal program will look similar to this:


The following is a basic example on how to decode the messages.
Modbus Read Holding Registers (FC=03)
Request
This command is requesting the content of analog output holding registers # 40108 to
40110 from the slave device with address 17.
11 03 006B 0003 7687
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
006B: The Data Address of the first register requested. (006B hex = 107 , + 40001 offset = input #40108 )
0003: The total number of registers requested. (read 3 registers 40108 to 40110)
7687: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check) for error checking.
Response
11 03 06 AE41 5652 4340 49AD
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
06: The number of data bytes to follow (3 registers x 2 bytes each = 6 bytes)
000F: The contents of register 40108 = 15
0059: The contents of register 40109 = 89
002F: The contents of register 40110 = 47
297B: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check).
Understanding what he SCADAPack E is transmitting and what the SCADAPack E is receiving at the “byte” level can help ensure you are sending and receiving the expected data.
More details on the MODBUSDIAG command can be found in the SCADAPack E “Command Line and Diagnostics Commands” help section of the Technical Reference manuals installed with SCADAPack E Utilities. The SCADAPack E Configuraiotn file used in this example is attached.
In cases where there might be a challenge communicating to a slave device, the Command line Interface and MODBUSDIAG may be used to troubleshoot the Modbus communication protocol. The Diagnostic Command Line Interface can only be accessed via Telnet or a serial port configured as “CMD Line”. The example below will use “CMD Line” port mode.
Use the MODBUSDIAG command to filter Modbus protocol diagnostics when you are in a diagnostic display session and the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master or a Modbus/TCP Client.
A Modbus RTU Master communicates with a Modbus RTU Slave using the Modbus RTU protocol over a serial port.
A Modbus/TCP Client communicates with a Modbus/TCP Server using the Modbus/TCP protocol over an Ethernet port, or using PPP/TCPIP over a serial port.
Hexadecimal format is used to display protocol data bytes.
To enter or return to a diagnostic display session, type DIAG at the command prompt.
Usage
MODBUSDIAG mode filter [filter ....]
Where: mode = ENABLE DISABLE
Where: filter = * TX RX ERROR TCP_CLIENT SERIAL_MASTER
Using diagnostics can impact system performance. As a result, you may want to disable diagnostics when not in use. The following system diagnostic filters can be individually enabled or disabled, and are retained in non-volatile memory.
| Filter | Description |
| * | Filters enabled or disabled. |
| TX | Displays Modbus protocol data transmitted by the Modbus RTU Master or Modbus/TCP Client. |
| RX | Displays Modbus protocol data received by the Modbus RTU Master or Modbus/TCP Client. |
| ERROR | Messages displayed when there are communication interruptions between the rPAC or RTU and the Modbus RTU Slave or Modbus/TCP Server. Message examples include no response, timeout, or connection success. |
| TCP_CLIENT | Displays receive and transmit data for the Modbus/TCP protocol when the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus/TCP Client. |
| SERIAL_MASTER | Displays receive and transmit data for the Modbus RTU protocol when the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master. |
Example
The system design will be as follows:
By connecting to the Command Line Interface port with a terminal program you can use the MODBUSDIAG command to see the Modbus messages to the slave device.
- Enable transmit and receive diagnostics on a serial port for MODBUSDIAG.
MODBUSDIAGS Enabled: TX RX ERROR SERIAL_MASTER
2. Start streaming diagnostics on the serial port (diag).
C:\>diag
Connecting to diagnostic display. Use <ESC> to disconnect
16:25:11.286 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:11.353 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:12.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:12.348 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:13.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:13.365 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
The actual windows in the terminal program will look similar to this:
The following is a basic example on how to decode the messages.
Modbus Read Holding Registers (FC=03)
Request
This command is requesting the content of analog output holding registers # 40108 to
40110 from the slave device with address 17.
11 03 006B 0003 7687
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
006B: The Data Address of the first register requested. (006B hex = 107 , + 40001 offset = input #40108 )
0003: The total number of registers requested. (read 3 registers 40108 to 40110)
7687: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check) for error checking.
Response
11 03 06 AE41 5652 4340 49AD
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
06: The number of data bytes to follow (3 registers x 2 bytes each = 6 bytes)
000F: The contents of register 40108 = 15
0059: The contents of register 40109 = 89
002F: The contents of register 40110 = 47
297B: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check).
Use Cases
Understanding what he SCADAPack E is transmitting and what the SCADAPack E is receiving at the “byte” level can help ensure you are sending and receiving the expected data.
More details on the MODBUSDIAG command can be found in the SCADAPack E “Command Line and Diagnostics Commands” help section of the Technical Reference manuals installed with SCADAPack E Utilities. The SCADAPack E Configuraiotn file used in this example is attached.
Released for:Schneider Electric Canada
With the introduction of the Modbus Scanner in E-Series Utilities 8.12.4, the SCADAPack E is able to be a Modbus Master for Modbus RTU or Modbus/TCP Client protocols.
In cases where there might be a challenge communicating to a slave device, the Command line Interface and MODBUSDIAG may be used to troubleshoot the Modbus communication protocol. The Diagnostic Command Line Interface can only be accessed via Telnet or a serial port configured as “CMD Line”. The example below will use “CMD Line” port mode.
Use the MODBUSDIAG command to filter Modbus protocol diagnostics when you are in a diagnostic display session and the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master or a Modbus/TCP Client.
A Modbus RTU Master communicates with a Modbus RTU Slave using the Modbus RTU protocol over a serial port.
A Modbus/TCP Client communicates with a Modbus/TCP Server using the Modbus/TCP protocol over an Ethernet port, or using PPP/TCPIP over a serial port.
Hexadecimal format is used to display protocol data bytes.
To enter or return to a diagnostic display session, type DIAG at the command prompt.
MODBUSDIAG mode filter [filter ....]
Where: mode = ENABLE DISABLE
Where: filter = * TX RX ERROR TCP_CLIENT SERIAL_MASTER
Using diagnostics can impact system performance. As a result, you may want to disable diagnostics when not in use. The following system diagnostic filters can be individually enabled or disabled, and are retained in non-volatile memory.
The system design will be as follows:

By connecting to the Command Line Interface port with a terminal program you can use the MODBUSDIAG command to see the Modbus messages to the slave device.
MODBUSDIAGS Enabled: TX RX ERROR SERIAL_MASTER
2. Start streaming diagnostics on the serial port (diag).
C:\>diag
Connecting to diagnostic display. Use <ESC> to disconnect
16:25:11.286 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:11.353 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:12.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:12.348 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:13.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:13.365 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
The actual windows in the terminal program will look similar to this:


The following is a basic example on how to decode the messages.
Modbus Read Holding Registers (FC=03)
Request
This command is requesting the content of analog output holding registers # 40108 to
40110 from the slave device with address 17.
11 03 006B 0003 7687
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
006B: The Data Address of the first register requested. (006B hex = 107 , + 40001 offset = input #40108 )
0003: The total number of registers requested. (read 3 registers 40108 to 40110)
7687: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check) for error checking.
Response
11 03 06 AE41 5652 4340 49AD
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
06: The number of data bytes to follow (3 registers x 2 bytes each = 6 bytes)
000F: The contents of register 40108 = 15
0059: The contents of register 40109 = 89
002F: The contents of register 40110 = 47
297B: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check).
Understanding what he SCADAPack E is transmitting and what the SCADAPack E is receiving at the “byte” level can help ensure you are sending and receiving the expected data.
More details on the MODBUSDIAG command can be found in the SCADAPack E “Command Line and Diagnostics Commands” help section of the Technical Reference manuals installed with SCADAPack E Utilities. The SCADAPack E Configuraiotn file used in this example is attached.
In cases where there might be a challenge communicating to a slave device, the Command line Interface and MODBUSDIAG may be used to troubleshoot the Modbus communication protocol. The Diagnostic Command Line Interface can only be accessed via Telnet or a serial port configured as “CMD Line”. The example below will use “CMD Line” port mode.
Use the MODBUSDIAG command to filter Modbus protocol diagnostics when you are in a diagnostic display session and the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master or a Modbus/TCP Client.
A Modbus RTU Master communicates with a Modbus RTU Slave using the Modbus RTU protocol over a serial port.
A Modbus/TCP Client communicates with a Modbus/TCP Server using the Modbus/TCP protocol over an Ethernet port, or using PPP/TCPIP over a serial port.
Hexadecimal format is used to display protocol data bytes.
To enter or return to a diagnostic display session, type DIAG at the command prompt.
Usage
MODBUSDIAG mode filter [filter ....]
Where: mode = ENABLE DISABLE
Where: filter = * TX RX ERROR TCP_CLIENT SERIAL_MASTER
Using diagnostics can impact system performance. As a result, you may want to disable diagnostics when not in use. The following system diagnostic filters can be individually enabled or disabled, and are retained in non-volatile memory.
| Filter | Description |
| * | Filters enabled or disabled. |
| TX | Displays Modbus protocol data transmitted by the Modbus RTU Master or Modbus/TCP Client. |
| RX | Displays Modbus protocol data received by the Modbus RTU Master or Modbus/TCP Client. |
| ERROR | Messages displayed when there are communication interruptions between the rPAC or RTU and the Modbus RTU Slave or Modbus/TCP Server. Message examples include no response, timeout, or connection success. |
| TCP_CLIENT | Displays receive and transmit data for the Modbus/TCP protocol when the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus/TCP Client. |
| SERIAL_MASTER | Displays receive and transmit data for the Modbus RTU protocol when the rPAC or RTU is operating as a Modbus RTU Master. |
Example
The system design will be as follows:
By connecting to the Command Line Interface port with a terminal program you can use the MODBUSDIAG command to see the Modbus messages to the slave device.
- Enable transmit and receive diagnostics on a serial port for MODBUSDIAG.
MODBUSDIAGS Enabled: TX RX ERROR SERIAL_MASTER
2. Start streaming diagnostics on the serial port (diag).
C:\>diag
Connecting to diagnostic display. Use <ESC> to disconnect
16:25:11.286 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:11.353 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:12.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:12.348 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
16:25:13.298 <--Outgoing Modbus RTU Request- 11 03 00 6B 00 03 76 87
16:25:13.365 -Incoming Modbus RTU Response--> 11 03 06 00 0F 00 59 00 2F 29 7B
The actual windows in the terminal program will look similar to this:
The following is a basic example on how to decode the messages.
Modbus Read Holding Registers (FC=03)
Request
This command is requesting the content of analog output holding registers # 40108 to
40110 from the slave device with address 17.
11 03 006B 0003 7687
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
006B: The Data Address of the first register requested. (006B hex = 107 , + 40001 offset = input #40108 )
0003: The total number of registers requested. (read 3 registers 40108 to 40110)
7687: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check) for error checking.
Response
11 03 06 AE41 5652 4340 49AD
11: The Slave Address (11 hex = address17 )
03: The Function Code 3 (read Analog Output Holding Registers)
06: The number of data bytes to follow (3 registers x 2 bytes each = 6 bytes)
000F: The contents of register 40108 = 15
0059: The contents of register 40109 = 89
002F: The contents of register 40110 = 47
297B: The CRC (cyclic redundancy check).
Use Cases
Understanding what he SCADAPack E is transmitting and what the SCADAPack E is receiving at the “byte” level can help ensure you are sending and receiving the expected data.
More details on the MODBUSDIAG command can be found in the SCADAPack E “Command Line and Diagnostics Commands” help section of the Technical Reference manuals installed with SCADAPack E Utilities. The SCADAPack E Configuraiotn file used in this example is attached.
Released for:Schneider Electric Canada

















