250 years of technology-driven revolutions towards smart energy
-
Industry 1.0
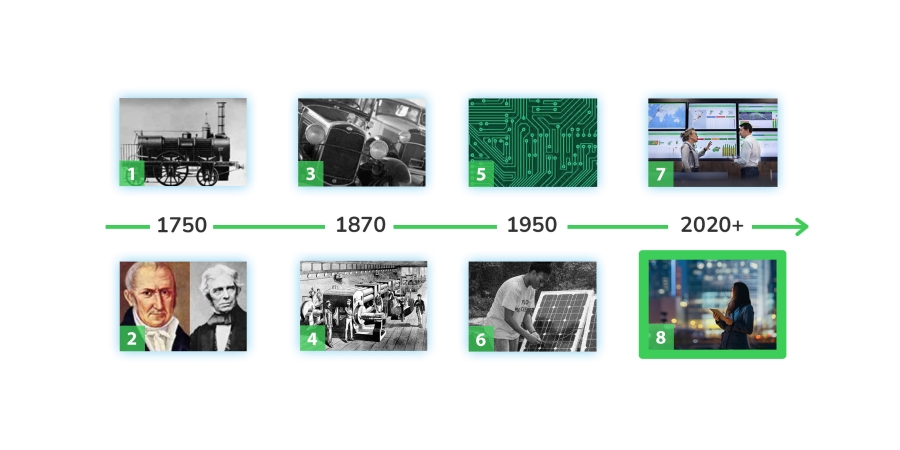
1The rise of technology in the 1750s, with the mechanization of steam and waterpower, is commonly recognized as Industry 1.0. -
Industry 2.0
2From the late 19th century, the world entered a new age of mass production that brought about the new chapter called Industry 2.0. -
Industry 3.0
3In the 1950s, the development of silicon led to the proliferation of automation and electronics giving rise to Industry 3.0. -
Industry 4.0
4The 21st century is the age of digital everywhere. Industry 4.0 is marked by the rise of smart machines fueled by Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and cloud computing and AI. -
Electricity 1.0
5In parallel, the electricity world has had its early pioneers such as Alessandro Volta, and Michael Faraday who furthered research on the practical use of electricity. We consider this as ‘Electricity 1.0’. -
Electricity 2.0
6The end of the 19th century also stands for mass electrification with electrical light deployed at an industrial scale, through the introduction of power plants. This is the beginning of Electricity 2.0. -
Electricity 3.0
7In the middle of the 20th century, the development of silicon facilitated the rise of early solar cells and solar panels, laying the groundwork for renewables. We call this Electricity 3.0. -
Electricity 4.0
8The 21st century gave birth to a new world of electricity with the convergence of digital and electric at scale. This is what we call Electricity 4.0.
Industry 1.0
1The rise of technology in the 1750s, with the mechanization of steam and waterpower, is commonly recognized as Industry 1.0.
Industry 2.0
2From the late 19th century, the world entered a new age of mass production that brought about the new chapter called Industry 2.0.
Industry 3.0
3In the 1950s, the development of silicon led to the proliferation of automation and electronics giving rise to Industry 3.0.
Industry 4.0
4The 21st century is the age of digital everywhere. Industry 4.0 is marked by the rise of smart machines fueled by Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and cloud computing and AI.
Electricity 1.0
5In parallel, the electricity world has had its early pioneers such as Alessandro Volta, and Michael Faraday who furthered research on the practical use of electricity. We consider this as ‘Electricity 1.0’.
Electricity 2.0
6The end of the 19th century also stands for mass electrification with electrical light deployed at an industrial scale, through the introduction of power plants. This is the beginning of Electricity 2.0.
Electricity 3.0
7In the middle of the 20th century, the development of silicon facilitated the rise of early solar cells and solar panels, laying the groundwork for renewables. We call this Electricity 3.0.
Electricity 4.0
8The 21st century gave birth to a new world of electricity with the convergence of digital and electric at scale. This is what we call Electricity 4.0.
Proven to be 3-5x more efficient than other sources, Electricity is the most efficient energy; it is also the best vector for decarbonization. By 2040, the share of electricity in everything we do will double, reaching at least 40% of final energy consumption; and six times more electricity will be generated from solar and wind.
Digital innovation makes energy smart
With digital innovation, the invisible becomes visible, eliminating waste and driving efficiency. Digital technology such as metering and monitoring enables us to see how we are using our energy. Adding to this with smart devices, apps, analytics, and software goes a step further and enables us to deploy smart energy more efficiently, meaning we can address a huge amount of untapped potential for energy savings.
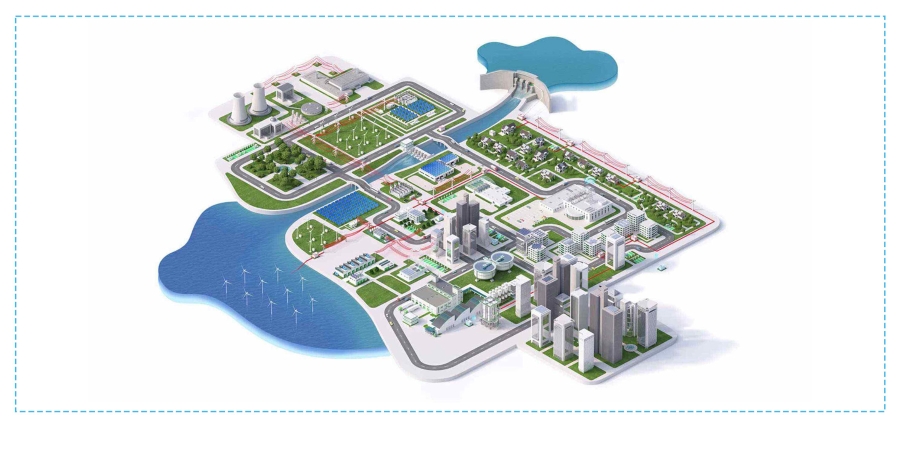
We build the New Electric World everywhere
With our products, systems, software, and services, we aim to deploy Electricity 4.0 in Homes, Buildings, Data Centers, Industries, Infrastructure, and Grids for more sustainable, resilient, and efficient future.
-
Grids of the Future
1Sustainable, Resilient, Efficient, Flexible -
Homes of the Future
2Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, More personal -
Data Centers of the Future
3Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, Adaptive -
Industries of the Future
4Sustainable, Efficient and resilient, People-centric, Next-generation -
Buildings of the Future
5Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, People-centric -
Partnerships of the future
6We are building the Partnerships of the Future underpinned by our core pillars of simplification, openness, and digitalization. -
Software
7Explore our software solutions and their capabilities in energy management and industrial automation applications. -
Services
8With industry-leading remote monitoring and a global base of experts, we can help you maintain and upgrade your critical assets.
Grids of the Future
1Sustainable, Resilient, Efficient, Flexible
Homes of the Future
2Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, More personal
Data Centers of the Future
3Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, Adaptive
Industries of the Future
4 Sustainable, Efficient and resilient, People-centric, Next-generation
Buildings of the Future
5Sustainable, Resilient, Hyper-efficient, People-centric
Partnerships of the future
6We are building the Partnerships of the Future underpinned by our core pillars of simplification, openness, and digitalization.
Software
7Explore our software solutions and their capabilities in energy management and industrial automation applications.
Services
8With industry-leading remote monitoring and a global base of experts, we can help you maintain and upgrade your critical assets.
Helping our customers on their journey to net zero
Schneider Electric is accelerating the pace at which we can all address climate change through agile digital innovation. We boost Innovation in our core whilst expanding in digital, end to end on all stages of the lifecycle.












